SEED CALCULATOR ❌
Number of Plants 0
Weight 0 oz
at 0 seeds per foot
Celery
Apium graveolensCertification
Color
Specialty
Heritage
Season
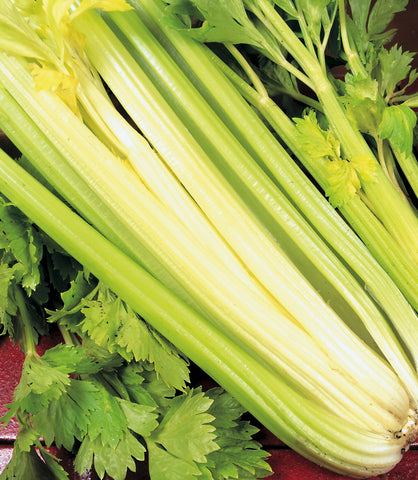
Domestication of Apium graveolens includes celery, celeriac and the wild type smallage. Celery originated between the eastern Mediterranean and the Himalayan foothills. Celery’s Latin genus name, Apium, is derived from Celtic meaning water. Originally a marsh species, celery is 95 percent water and is a good fibrous diet food. Its species, graveolens, means heavily scented. Its first use was for its seed in Egypt, Greece and the Roman Empire as a diuretic for intestinal ailments and as an aphrodisiac. As a vegetable, the earliest domestication of celery as a leafy plant with non-succulent stems like smallage, which is still widely cultivated across Asia as salad green and potherb. The development of modern celery started in Italy and France in the 16th century.
There are three main forms of Apium graveolens. Smallage or wild celery is also known as leaf celery and the leaves and stems are all used. From this wild form comes Celery, A. graveolens var. dulce, with its succulent leaf stems and is popular vegetable the world over. Parcel, A. graveolens var. secalinum is a leaf celery with finely cut parsley looking leaves. Delicious celery recipes.
Companions: leeks, tomatoes, cauliflower, cabbage, bush beans

-
Price List
Domestication of Apium graveolens includes celery, celeriac and the wild type smallage. Celery originated between the eastern Mediterranean and the Himalayan foothills. Celery’s Latin genus name, Apium, is derived from Celtic meaning water. Originally a marsh species, celery is 95 percent water and is a good fibrous diet food. Its species, graveolens, means heavily scented. Its first use was for its seed in Egypt, Greece and the Roman Empire as a diuretic for intestinal ailments and as an aphrodisiac. As a vegetable, the earliest domestication of celery as a leafy plant with non-succulent stems like smallage, which is still widely cultivated across Asia as salad green and potherb. The development of modern celery started in Italy and France in the 16th century.
There are three main forms of Apium graveolens. Smallage or wild celery is also known as leaf celery and the leaves and stems are all used. From this wild form comes Celery, A. graveolens var. dulce, with its succulent leaf stems and is popular vegetable the world over. Parcel, A. graveolens var. secalinum is a leaf celery with finely cut parsley looking leaves. Delicious celery recipes.
Companions: leeks, tomatoes, cauliflower, cabbage, bush beans








